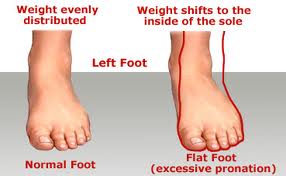
Overview

Fallen arches, also know as having flat feet, or pes planus, refers to the collapsing of the foot?s arch so that it is no longer curved properly or adequately supportive. The condition can cause foot pain, fatigue and affect gait, which can create strain on the knees, ankles legs and hips. Fallen arches can occur naturally from birth, or can be attributed to the rolling in of the foot and ankle while running (overpronation).
Causes
The arches of most individuals are fully developed by the age of 12 to 13. While some people are born with flat arches, for others, the arches fall over time. The tibial tendon, which runs along the inside of the ankle from above the ankle to the arch, can weaken with age and with heavy activity. The posterior tendon, main support structure for the arch, can become inflamed (tendonitis) or even tear if overloaded. For women, wearing high heels can affect the Achilles tendon and alter the structure and function of the ankle. The posterior tibial tendon may compensate for this stress and break down, causing the arches to fall. Obesity is another contributing factor, as well as a serious injury to the ankle or foot, arthritis and bad circulation such as occurs with diabetes.
Symptoms
Not everyone who has flat feet experiences symptoms. Others, however, feel persistent pain in their feet and wearing shoes can prove additionally painful. Others only feel symptoms when they walk more than normal, go jogging or participate in a sport that involves running or kicking.
Diagnosis
You can test yourself to see if you have flat feet or fallen arches by using a simple home experiment. First, dip your feet in water. Then step on a hard flat surface, like a dry floor or a piece of paper on the floor, where your footprints will show. Step away and examine your foot prints. If you see complete/full imprints of your feet on the floor, you may have fallen arches. However, it?s important to seek a second option from a podiatrist if you suspect you have fallen arches so they can properly diagnose and treat you.
fallen arches surgery
Non Surgical Treatment
During walking and running, there is a small natural inward drop (slight pronation) that is part of the spring and propulsion. Allowing exaggerated sagging is like rounding your shoulders too much. Legs and feet have posture that you can control yourself. Use your own muscles and get free built-in exercise and arch support all day, and stop painful poor positioning. Some people with existing abnormality or growths in the ball of the foot will roll inward (or outward) to get the pressure off the deformed area because standing straight hurts. See your doctor first. Remember, don't force. If it hurts, it's wrong. All you are doing is learning how to stand neutral, not tilted so much that you compress the joints. The concept is to hold your feet in the same healthful position that shoe supports would. It is like an ice skater holds their skates straight at the ankle, not angled.
Surgical Treatment

Surgery is typically offered as a last resort in people with significant pain that is resistant to other therapies. The treatment of a rigid flatfoot depends on its cause. Congenital vertical talus. Your doctor may suggest a trial of serial casting. The foot is placed in a cast and the cast is changed frequently to reposition the foot gradually. However, this generally has a low success rate. Most people ultimately need surgery to correct the problem. Tarsal coalition. Treatment depends on your age, extent of bone fusion and severity of symptoms. For milder cases, your doctor may recommend nonsurgical treatment with shoe inserts, wrapping of the foot with supportive straps or temporarily immobilizing the foot in a cast. For more severe cases, surgery is necessary to relieve pain and improve the flexibility of the foot. Lateral subtalar dislocation. The goal is to move the dislocated bone back into place as soon as possible. If there is no open wound, the doctor may push the bone back into proper alignment without making an incision. Anesthesia is usually given before this treatment. Once this is accomplished, a short leg cast must be worn for about four weeks to help stabilize the joint permanently. About 15% to 20% of people with lateral subtalar dislocation must be treated with surgery to reposition the dislocated bone.

Fallen arches, also know as having flat feet, or pes planus, refers to the collapsing of the foot?s arch so that it is no longer curved properly or adequately supportive. The condition can cause foot pain, fatigue and affect gait, which can create strain on the knees, ankles legs and hips. Fallen arches can occur naturally from birth, or can be attributed to the rolling in of the foot and ankle while running (overpronation).
Causes
The arches of most individuals are fully developed by the age of 12 to 13. While some people are born with flat arches, for others, the arches fall over time. The tibial tendon, which runs along the inside of the ankle from above the ankle to the arch, can weaken with age and with heavy activity. The posterior tendon, main support structure for the arch, can become inflamed (tendonitis) or even tear if overloaded. For women, wearing high heels can affect the Achilles tendon and alter the structure and function of the ankle. The posterior tibial tendon may compensate for this stress and break down, causing the arches to fall. Obesity is another contributing factor, as well as a serious injury to the ankle or foot, arthritis and bad circulation such as occurs with diabetes.
Symptoms
Not everyone who has flat feet experiences symptoms. Others, however, feel persistent pain in their feet and wearing shoes can prove additionally painful. Others only feel symptoms when they walk more than normal, go jogging or participate in a sport that involves running or kicking.
Diagnosis
You can test yourself to see if you have flat feet or fallen arches by using a simple home experiment. First, dip your feet in water. Then step on a hard flat surface, like a dry floor or a piece of paper on the floor, where your footprints will show. Step away and examine your foot prints. If you see complete/full imprints of your feet on the floor, you may have fallen arches. However, it?s important to seek a second option from a podiatrist if you suspect you have fallen arches so they can properly diagnose and treat you.
fallen arches surgery
Non Surgical Treatment
During walking and running, there is a small natural inward drop (slight pronation) that is part of the spring and propulsion. Allowing exaggerated sagging is like rounding your shoulders too much. Legs and feet have posture that you can control yourself. Use your own muscles and get free built-in exercise and arch support all day, and stop painful poor positioning. Some people with existing abnormality or growths in the ball of the foot will roll inward (or outward) to get the pressure off the deformed area because standing straight hurts. See your doctor first. Remember, don't force. If it hurts, it's wrong. All you are doing is learning how to stand neutral, not tilted so much that you compress the joints. The concept is to hold your feet in the same healthful position that shoe supports would. It is like an ice skater holds their skates straight at the ankle, not angled.
Surgical Treatment

Surgery is typically offered as a last resort in people with significant pain that is resistant to other therapies. The treatment of a rigid flatfoot depends on its cause. Congenital vertical talus. Your doctor may suggest a trial of serial casting. The foot is placed in a cast and the cast is changed frequently to reposition the foot gradually. However, this generally has a low success rate. Most people ultimately need surgery to correct the problem. Tarsal coalition. Treatment depends on your age, extent of bone fusion and severity of symptoms. For milder cases, your doctor may recommend nonsurgical treatment with shoe inserts, wrapping of the foot with supportive straps or temporarily immobilizing the foot in a cast. For more severe cases, surgery is necessary to relieve pain and improve the flexibility of the foot. Lateral subtalar dislocation. The goal is to move the dislocated bone back into place as soon as possible. If there is no open wound, the doctor may push the bone back into proper alignment without making an incision. Anesthesia is usually given before this treatment. Once this is accomplished, a short leg cast must be worn for about four weeks to help stabilize the joint permanently. About 15% to 20% of people with lateral subtalar dislocation must be treated with surgery to reposition the dislocated bone.



 Morton's neuroma, also called Morton's metatarsalgia, Morton's disease, Morton's neuralgia, Morton metatarsalgia, Morton nerve entrapment, plantar neuroma, or intermetatarsal neuroma is a benign (non-cancerous) growth of nerve tissue (neuroma) that develops in the foot, usually between the third and fourth toes (an intermetatarsal plantar nerve, most commonly of the third and fourth intermetatarsal spaces). It is a common, painful condition.
Morton's neuroma, also called Morton's metatarsalgia, Morton's disease, Morton's neuralgia, Morton metatarsalgia, Morton nerve entrapment, plantar neuroma, or intermetatarsal neuroma is a benign (non-cancerous) growth of nerve tissue (neuroma) that develops in the foot, usually between the third and fourth toes (an intermetatarsal plantar nerve, most commonly of the third and fourth intermetatarsal spaces). It is a common, painful condition.




 A bunion is a bony lump on the side of your foot, which develops when your big toe starts to angle towards your second toe. The bunion will eventually cause you discomfort and pain. The skin over the lump can become red, blistered or infected. A fluid-filled space called a bursa may also develop under your skin in this area and this can be painful if it becomes inflamed. This is called bursitis. The deformity of your big toe combined with a bunion is sometimes referred to as hallux valgus.
A bunion is a bony lump on the side of your foot, which develops when your big toe starts to angle towards your second toe. The bunion will eventually cause you discomfort and pain. The skin over the lump can become red, blistered or infected. A fluid-filled space called a bursa may also develop under your skin in this area and this can be painful if it becomes inflamed. This is called bursitis. The deformity of your big toe combined with a bunion is sometimes referred to as hallux valgus.