Overview
A person with flat feet (fallen arches) has low arches or no arches at all. Most cases don't cause problems and treatment isn't usually needed. The arch, or instep, is the inside part of the foot that's usually raised off the ground when you stand, while the rest of the foot remains flat on the ground. Most people have a noticeable space on the inner part of their foot (the arch). The height of the arch varies from person to person.
Causes
Having low or no arches is normal for some people. In these cases, flat feet are usually inherited and the feet are fairly flexible. Occasionally, flat feet can be caused by an abnormality that develops in the womb, such as a problem with a joint or where two or more bones are fused together. This is known as tarsal coalition and results in the feet being flat and stiff. Flat feet that develop in later life can be caused by a condition that affects the joints, such as arthritis, or an injury to a muscle, tendon or joint in the foot.
Symptoms
Go to a podiatrist at the first sign of symptoms. Besides pain on the bottom of the foot, additional symptoms may include burning sensation in arch, difficulty standing on tiptoes, inflammation, more pain after sleeping or resting, redness, heat, localized pain in the ball of the foot, sharp or shooting pain in the toes, pain that increases when toes are flexed, tingling or numbness in the toes, aching, pain that increases when walking barefoot, pain that increases when walking on hard surfaces, pain the increases when standing (putting weight on your feet) or moving around and decreases when immobile, skin Lesions, it?s important to get a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Let?s go over the possible causes of the pain.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of a plantar plate tear can often be challenging due to the complex nature of the anatomy of the foot. Careful history taking and an examination of the area of pain is required to determine the extent and cause of the tear. If necessary, further investigations such as x-rays or diagnostic ultrasound may be ordered by your podiatrist to help evaluate the severity of the problem.
Non Surgical Treatment
The initial treatment for arch pain, especially if it is of sudden onset is the use of ice to reduce the swelling. Later heat and anti-inflammatory gels can be a big help. Activity should be modified, if you stand a lot at work, see if you can using seating more, if you run a lot, consider swimming or cycling for a while. Use footwear that is supportive in the midfoot and heel area.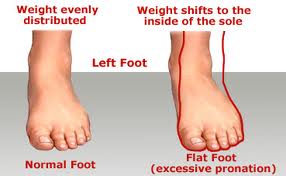
Surgical Treatment
Tendon transfers: Too much pull of certain muscles and tendons is often the cause of the deformity related with a cavus foot. Moving one of these muscles or tendons may help the foot work better. In addition, patients with a cavus foot may have weakness in moving the foot up, which is sometimes called a foot drop. In these cases, a tendon from the back of the ankle may be moved to the top of the foot to help improve strength. Correcting the deformity of the foot may not be possible with soft tissue procedures alone. In these instances, one or more bone cuts (osteotomies) may be needed. Instead of a bone cut, a fusion (arthrodesis) procedure may be used. A fusion removes the joint between two bones so they grow together over time. During a fusion the bones may be held in place with plates or screws. Calcaneal osteotomy: This procedure is performed to bring the heel bone back under the leg. This is needed if correction of the deformity in the front of the foot does not also correct the back of the foot or ankle. A calcaneal osteotomy can be performed several ways and is often held in place with one or more screws. Sometimes patients have a deformity that has caused damage to the joints. In these cases, soft tissue procedures or bone cuts may not be enough, and it may be necessary to eliminate the joint. Clawed toes are a common problem with cavus foot deformity. This can be treated with tendon surgery, fusion or removal of part of the toe bones. Following surgery the toes are often temporarily held in place with pins.
Prevention
The best method for preventing plantar fasciitis is stretching. The plantar fascia can be stretched by grabbing the toes, pulling the foot upward and holding for 15 seconds. To stretch the calf muscles, place hands on a wall and drop affected leg back into a lunge step while keeping the heel of the back leg down. Keep the back knee straight for one stretch and then bend the knee slightly to stretch a deeper muscle in the calf. Hold stretch for 15 seconds and repeat three times.
Stretching Exercises
Massage therapy is a great way to loosen muscles and help improve mobility in in your feet. As many people with foot pain have discovered, tight muscles in your legs or back can lead to tense foot muscles. All those muscles are connected, so tension in your back can cause tension in your legs which can pull the tendons in your feet and cause stiffness and pain. Getting acupuncture or a professional full body massage are probably the best ways to deal with this, but there are also some simple tricks you can do at home to help keep muscles limber. These are great for loosening up and improving circulation, both before and after exercise. Place a tennis ball under the arch of your bare foot and roll it around, stretching the muscles in your foot and promoting blood flow. You can also roll the ball under your calves and upper legs to work out stiffness and knots. If you feel the tennis ball is too easy, try a lacrosse ball for deeper massaging. This is also demonstrated in the exercise video above. Use a foam roller, those big overpriced rolls of foam that are now available in every department and sporting goods store are fantastic for self-massage (why a roll of foam costs $30 is beyond us, but they do work wonders-our advice is to not waste money on the more expensive fancy grooved ones because even the simplest rollers work great). The exercises you can do with foam rollers seem to be endless, and there are literally hundreds of free videos online showing how to use them to massage every part of your body. Here's one we picked out that specifically targets foot and leg muscles related to arches and plantar fasciitis.
A person with flat feet (fallen arches) has low arches or no arches at all. Most cases don't cause problems and treatment isn't usually needed. The arch, or instep, is the inside part of the foot that's usually raised off the ground when you stand, while the rest of the foot remains flat on the ground. Most people have a noticeable space on the inner part of their foot (the arch). The height of the arch varies from person to person.

Causes
Having low or no arches is normal for some people. In these cases, flat feet are usually inherited and the feet are fairly flexible. Occasionally, flat feet can be caused by an abnormality that develops in the womb, such as a problem with a joint or where two or more bones are fused together. This is known as tarsal coalition and results in the feet being flat and stiff. Flat feet that develop in later life can be caused by a condition that affects the joints, such as arthritis, or an injury to a muscle, tendon or joint in the foot.
Symptoms
Go to a podiatrist at the first sign of symptoms. Besides pain on the bottom of the foot, additional symptoms may include burning sensation in arch, difficulty standing on tiptoes, inflammation, more pain after sleeping or resting, redness, heat, localized pain in the ball of the foot, sharp or shooting pain in the toes, pain that increases when toes are flexed, tingling or numbness in the toes, aching, pain that increases when walking barefoot, pain that increases when walking on hard surfaces, pain the increases when standing (putting weight on your feet) or moving around and decreases when immobile, skin Lesions, it?s important to get a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Let?s go over the possible causes of the pain.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of a plantar plate tear can often be challenging due to the complex nature of the anatomy of the foot. Careful history taking and an examination of the area of pain is required to determine the extent and cause of the tear. If necessary, further investigations such as x-rays or diagnostic ultrasound may be ordered by your podiatrist to help evaluate the severity of the problem.
Non Surgical Treatment
The initial treatment for arch pain, especially if it is of sudden onset is the use of ice to reduce the swelling. Later heat and anti-inflammatory gels can be a big help. Activity should be modified, if you stand a lot at work, see if you can using seating more, if you run a lot, consider swimming or cycling for a while. Use footwear that is supportive in the midfoot and heel area.

Surgical Treatment
Tendon transfers: Too much pull of certain muscles and tendons is often the cause of the deformity related with a cavus foot. Moving one of these muscles or tendons may help the foot work better. In addition, patients with a cavus foot may have weakness in moving the foot up, which is sometimes called a foot drop. In these cases, a tendon from the back of the ankle may be moved to the top of the foot to help improve strength. Correcting the deformity of the foot may not be possible with soft tissue procedures alone. In these instances, one or more bone cuts (osteotomies) may be needed. Instead of a bone cut, a fusion (arthrodesis) procedure may be used. A fusion removes the joint between two bones so they grow together over time. During a fusion the bones may be held in place with plates or screws. Calcaneal osteotomy: This procedure is performed to bring the heel bone back under the leg. This is needed if correction of the deformity in the front of the foot does not also correct the back of the foot or ankle. A calcaneal osteotomy can be performed several ways and is often held in place with one or more screws. Sometimes patients have a deformity that has caused damage to the joints. In these cases, soft tissue procedures or bone cuts may not be enough, and it may be necessary to eliminate the joint. Clawed toes are a common problem with cavus foot deformity. This can be treated with tendon surgery, fusion or removal of part of the toe bones. Following surgery the toes are often temporarily held in place with pins.
Prevention
The best method for preventing plantar fasciitis is stretching. The plantar fascia can be stretched by grabbing the toes, pulling the foot upward and holding for 15 seconds. To stretch the calf muscles, place hands on a wall and drop affected leg back into a lunge step while keeping the heel of the back leg down. Keep the back knee straight for one stretch and then bend the knee slightly to stretch a deeper muscle in the calf. Hold stretch for 15 seconds and repeat three times.
Stretching Exercises
Massage therapy is a great way to loosen muscles and help improve mobility in in your feet. As many people with foot pain have discovered, tight muscles in your legs or back can lead to tense foot muscles. All those muscles are connected, so tension in your back can cause tension in your legs which can pull the tendons in your feet and cause stiffness and pain. Getting acupuncture or a professional full body massage are probably the best ways to deal with this, but there are also some simple tricks you can do at home to help keep muscles limber. These are great for loosening up and improving circulation, both before and after exercise. Place a tennis ball under the arch of your bare foot and roll it around, stretching the muscles in your foot and promoting blood flow. You can also roll the ball under your calves and upper legs to work out stiffness and knots. If you feel the tennis ball is too easy, try a lacrosse ball for deeper massaging. This is also demonstrated in the exercise video above. Use a foam roller, those big overpriced rolls of foam that are now available in every department and sporting goods store are fantastic for self-massage (why a roll of foam costs $30 is beyond us, but they do work wonders-our advice is to not waste money on the more expensive fancy grooved ones because even the simplest rollers work great). The exercises you can do with foam rollers seem to be endless, and there are literally hundreds of free videos online showing how to use them to massage every part of your body. Here's one we picked out that specifically targets foot and leg muscles related to arches and plantar fasciitis.
